In today’s fast-paced digital economy, the payments landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation. Businesses are increasingly turning to innovative solutions to streamline their payment processes and enhance customer experiences. One of the most transformative strategies gaining traction is payment orchestration. This approach integrates various payment services into a unified platform, optimising efficiency and driving growth. Payment orchestration is revolutionising how businesses manage payments, paving the way for a more efficient, flexible, and customer- centric payment ecosystem.
Understanding Payment Orchestration
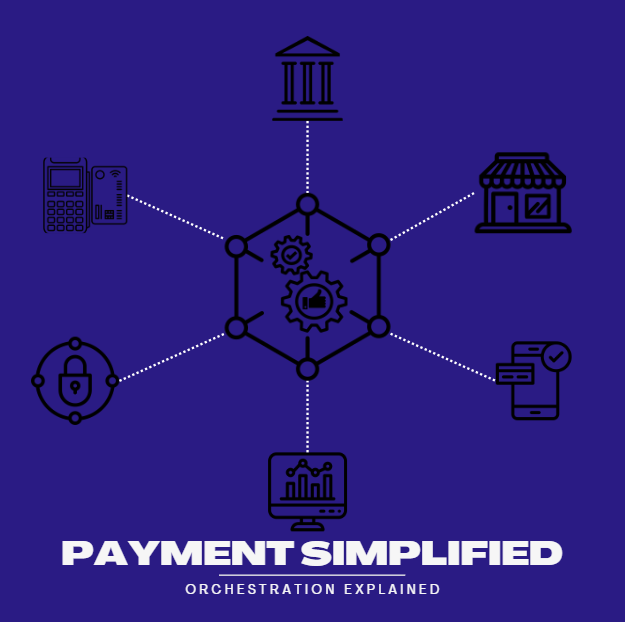
At its core, payment orchestration refers to the strategic coordination of multiple payment services and technologies to create a unified and streamlined payment experience. It involves integrating various payment gateways, processors, fraud prevention tools, and other payment-related services into a single platform or system. This integration allows businesses to manage all their payment activities from one central hub, optimising the payment process across different channels and touch points.
The Evolution of Payment Orchestration
Traditionally, businesses managed payments through individual payment gateways or processors, each with its own set of features, interfaces, and integration requirements. This fragmented approach often led to inefficiencies, higher costs, and a lack of flexibility in adapting to new payment trends.
Payment orchestration emerged as a response to these challenges. By centralising and automating
payment management, businesses can achieve several key benefits:
- Centralised Management: Businesses can now manage all payment activities from a single platform, reducing complexity and streamlining operations.
- Enhanced Flexibility and Scalability: Businesses can easily add, remove, or switch payment providers without disrupting their operations. This flexibility is crucial in a rapidly evolving payments landscape where new payment methods and technologies are constantly emerging.
- Cost Efficiency: By optimising payment routing and reducing reliance on multiple providers, this can help businesses lower transaction costs and increase profitability. The ability to negotiate better terms with payment providers and leverage competitive pricing models further enhances cost efficiency.
- Improved Fraud Prevention: Integration with multiple fraud prevention tools provides a layered approach to detecting and mitigating fraud.
- Unified Customer Experience: Deliver a consistent, convenient checkout across all channel and increase satisfaction and loyalty.
- Real-time insights: Unified reporting and analytics enables better decision-making, helps identify trends and opportunities, and provides valuable insights into customer behaviour and preferences.
- Global Reach: For businesses operating internationally, payment orchestration simplifies the process of managing cross-border transactions and integrating with local payment methods. This global reach helps businesses expand their market presence and cater to a diverse customer base.
- Streamlined Compliance: Navigating the complex regulatory environment of the payments industry can be challenging. Payment orchestration platforms help businesses stay compliant with various regulations and standards, such as PCI-DSS and GDPR, by providing built-in compliance features and regularly updating their systems to meet regulatory requirements.
Who Can Benefit from Payment Orchestration
Payment orchestration offers a range of benefits across various sectors and business models. Here are key use cases for payment orchestration across various industries and how they can benefit from this transformative strategy:
- Queue Busting
- Use Case: Equip floor staff with mobile point-of-sale (POS) systems to process payments anywhere in the store, reducing long checkout lines and improving customer satisfaction.
- Applicable Industries: Retail, Hospitality.
- Impact: Reduces wait times, enhances customer experience, and improves efficiency during peak shopping hours by turning every staff member into a sales agent.
- Self-Checkout Kiosks
- Use Case: Integrate payment processing with self-service kiosks to empower customers with faster, more convenient checkout options.
- Applicable Industries: Retail, Quick Service Restaurants (QSRs), Grocery.
- Impact: Minimises wait times, reduces staffing needs, and provides a more autonomous shopping experience for customers.
- Endless Aisles
- Use Case: Enable customers to browse and order a wider variety of items directly from the store, even if they’re not available on physical shelves.
- Applicable Industries: Retail, Electronics, Furniture.
- Impact: Extends product availability beyond in-store stock, increasing sales and customer satisfaction by offering more choices.
- Click and Collect
- Use Case: Allow customers to order items online and conveniently pick them up in-store.
- Applicable Industries: Retail, Grocery, Pharmaceuticals.
- Impact: Combines the convenience of online shopping with the immediacy of in-store pickup, catering to customer preferences for flexibility.
- Webrooming 2.0 with Instant Returns
- Use Case: Allow customers to research and buy products online, experience and pick them up in-store, and return them instantly for refunds if needed.
- Applicable Industries: Fashion, Electronics, Home Goods.
- Impact: Provides the best of both online and in-store shopping experiences, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty through seamless, instant returns.
- Curbside Pickup
- Use Case: Offer customers the convenience of ordering online and picking up their purchases without leaving their cars.
- Applicable Industries: Grocery, Retail, QSRs (Quick Service Restaurant).
- Impact: Enhances customer convenience, especially for those who prefer contactless service or are in a rush.
- Cross-Channel Returns
- Use Case: Enable customers to return items purchased online in-store and vice versa.
- Applicable Industries: Retail, Fashion, Consumer Electronics.
- Impact: Provides flexibility for customers, driving satisfaction and encouraging repeat purchases by simplifying returns.
- International Expansion
- Use Case: Support multiple currencies and payment methods for customers across the globe.
- Applicable Industries: eCommerce, Travel, Luxury Goods.
- Impact: Facilitates global growth by providing a frictionless shopping experience to international customers, adapting to their preferred payment methods and currencies.
In Conclusion
The future of payment orchestration is poised for significant evolution both globally and within South Africa, driven by advancements in technology and shifting consumer expectations. Globally, businesses are increasingly adopting payment orchestration platforms to streamline their payment processes, enhance customer experiences, and integrate multiple payment methods seamlessly. The rise of digital wallets, cryptocurrencies, and artificial intelligence is set to redefine transaction experiences, promoting greater efficiency and security.
In South Africa, the growing digital landscape and the increasing adoption of e-Commerce present unique opportunities for payment orchestration. As businesses navigate a diverse consumer base with varying payment preferences, orchestrated solutions will enable them to manage multiple payment gateways, support local and alternative payment methods, and facilitate seamless cross- border transactions. The emphasis on financial inclusion and accessibility will drive South African companies to embrace innovative payment solutions, positioning payment orchestration as a key differentiator in a competitive market.
Ultimately, both globally and in South Africa, payment orchestration will be crucial in shaping a more interconnected, customer-centric financial ecosystem, paving the way for enhanced flexibility, efficiency, and growth in the payments landscape.